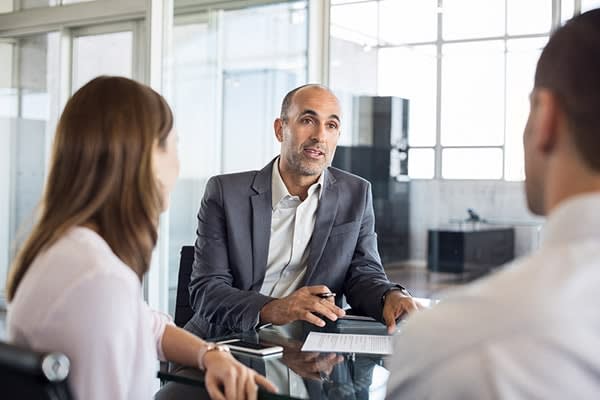
Introduction to ACCA
What is the ACCA?
The Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA) is a global professional accounting body that offers internationally recognized qualifications and certifications in accounting, finance, and business management.
Importance of ACCA
Why is ACCA qualification important?
Candidates with the ACCA credential have an advantage in the global job market due to the organization’s widespread recognition. Members of ACCA are in high demand among businesses because of the level of skill and professionalism they possess. Because they possess such a diverse set of abilities and knowledge, ACCA members are certain to be well-rounded professionals who are capable of excelling in a wide variety of accounting and financial roles.
Earning an ACCA qualification opens up a world of opportunities for you; from opting for another qualification or pursuing a master’s degree, to setting up your own business, the possibilities are endless. However, if you want to work for an organization or look for accounting jobs, there are plenty of ACCA jobs to choose from too.
Read the following blog post to find out more about the exciting job roles that await you, post your ACCA qualification.
What are the 10 job roles post ACCA?
- Financial Accountant: Financial accounting refers to the method of recording, summarizing, and interpreting the transactions that occur as a result of business operations, over a specific period of time. Financial accountants analyze financial information with the assistance of cash flow statements and balance sheets. They are also responsible for preparing the organization’s financial statements for external parties like tax and regulations authorities, creditors, shareholders and investors. You will also be expected to create business strategies to increase revenue and profit.
- Management accountant: The process of assessing operations and business costs that are required to prepare financial reports is the basis of management accounting. These reports assist managers in setting organizational goals. Management accountants are responsible for recognizing, measuring, assessing, and communicating the financial information of an organization. They analyze critical organizational information and data that is used to assist the management in taking important business decisions. Although their role may seem similar to financial accountants who provide financial statements to external entitites; management accountants differ as they analyze information for the internal management of the organization to help measure performance and the strategies employed.
- Corporate treasurer: Corporate treasurers are responsible for ensuring that organizations have the capital to meet their obligations. Their roles also include shaping financial policies and strategies, advising on investment opportunities, arranging funds for expansion purposes and managing financial risk. On top of these jobs, corporate treasures assess financial markets and acquisitions and mergers, while also negotiating lines of credit. This job role consists of five key elements, which are:
- Capital markets and funding: This includes assessing and acquiring the funding methods that are available to an organization.
- Liquidity and cash management: This element ensures that the organization’s ‘cash needs’ are met in an effective manner.
- Corporate financial management: Ensuring that an organization’s financial, management and corporate strategies are aligned with organizational goals refers to corporate financial management.
- Risk management: Risk management is the process of recognizing, assessing and mitigating the risks that an organization might encounter. Corporate treasurers are also responsible for ensuring that appropriate risk management techniques are being employed by the organization.
- Treasury operations: This involves keeping up-to-date with the latest financial developments, communicating with investors and bankers to encourage positive working relationships and providing solutions to financial problems by using their in-depth treasury knowledge.
- Assistant accountant: This is a junior accounting role and it falls under the command of the financial director or financial controller in an organization. The job responsibilities vary from one organization to another, but the most common duties involved are bookkeeping, handling the organization’s financial accounts. They also manage the incoming payments, record them and prepare financial and salary statements.
- Financial controller: Financial controllers, otherwise know as ‘financial comptrollers’ are usually senior executives in an organization. They are usually in charge of an organization’s accounting department, ensuring that the financial records and books of an organization are maintained as per business and legal requirements. These controllers are mainly concerned with historical records but may perform other duties such as compliance audits, budgeting process and assessing financial data.
- Finance manager: These people are accountable for an organization’s financial health. Financial managers manage different areas in an organization’s finance division, such as financial analysis, financial accounting and management accounting. This job role includes other duties such as:
- Creating business reports, financial statements and financial forecasts;
- Examining the organization’s financial details to ensure it is in line with the legal requirements;
- Overseeing the assistant accountants who prepare the organization’s financial statements;
- Analyzing the organization’s financial reports to find solutions for the reduction of costs;
- Evaluating market trends to recognize expansion or investment opportunities;
- Helping the management in making important financial decisions.
- Forensic accountant: Forensic accounting involves the use of accounting, auditing and investigative skills to examine an organization’s financial reports and statements. This job role is mainly present in professional services organizations. Their duty is to examine if there is any fraudulent activity present in the finances of an organization. Other roles include:
- Closely examining the assets, liabilities and resources of an organization;
- Ensuring the organization’s financial statements and records are accurate;
- Collecting an organization’s financial information and auditing this information;
- Carrying out forensic investigations into the finances of an organization;
- Preparing forensic reports that are to be used in court as supporting evidence.
- Chief financial officer (CFO): A CFO is a senior executive who is responsible for managing the financial operations in an organization. In an organisation, the CFO has three main responsibilities, which include:
- Management and budgeting: In a small organization, the CFO is responsible for monitoring budgets, cash flows, salaries and investments. In larger organizations, the chief financial officer oversees the preparation of budgets, allocating resources in an effective manner and deciding pay-scales for employees.
- Accounting and reporting: This senior executive manages accounts and prepares monthly or annual financial reports and statements in small organizations. In large organizations, they have more financial analysis and management duties.
- Strategy and planning: Chief financial officers also collaborate with chief executive officers and the board members to assess productivity and improve efficiency. This is done using their in-depth knowledge of funding sources, markets and general economic viewpoint.
- Auditor: An auditor examines and authenticates the precision of an organization’s financial and operational records and statements. Auditors usually work for large accounting firms, some of them include Deloitte, Ernst & Young (EY), PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) and KPMG. They verify if the financial records of an organization are in agreement with the regulatory framework. Audited financial statements instil confidence in investors and shareholders and it also helps in reducing organizational risk.
- Tax specialist: This job role is usually found in professional accounting or services firms. The duty of a tax specialist is to advise clients on tax law at local and international levels and also personally and professionally. They are also responsible for assisting organizations in meeting their taxation requirements.
What is the salary earned by an ACCA professional?
Accounting qualifications such as ACCA are considered to be lucrative because ACCA qualified professionals earn high salary packages. According to payscale.com, ACCA qualified professionals can earn between $45,000 CAD and $125,000 CAD annually. The salary earned depends upon the job role of the professional and the organization they are working for.
If you are interested in pursuing an accountancy qualification, the Toronto School of Management (TSoM) offers a preparatory course for ACCA Examination. To find out more, click here.
FAQs
- What is the highest salary for an ACCA professional?
The salary of an ACCA qualified professional varies depending on different factors. However, the salary of a chartered accountant in Canada could reach up to $76,818 per year. - Who earns more, CPA or ACCA professionals?
The income potential of a CPA or an ACCA qualified professional is determined by a variety of criteria, including experience, industry, and employment category. - Is ACCA qualification recognized globally?
Yes, the ACCA qualification is globally recognized. It is recognized by regulatory agencies and countries all around the world, ensuring that members meet necessary standards in the fields of accounting and finance. - What are the job roles available after ACCA qualification?
Individuals who complete the ACCA certificate can pursue a number of employment roles in accounting and finance. Financial analyst, audit manager, tax manager, financial controller, and chief financial officer (CFO) are some of the employment responsibilities open to ACCA qualified professionals. - What is ACCA qualification?
The ACCA qualification is widely regarded as one of the most renowned and respected qualifications in the field of accounting and finance. It is designed to provide people the skills and knowledge they need to be successful in a variety of accounting and finance roles.